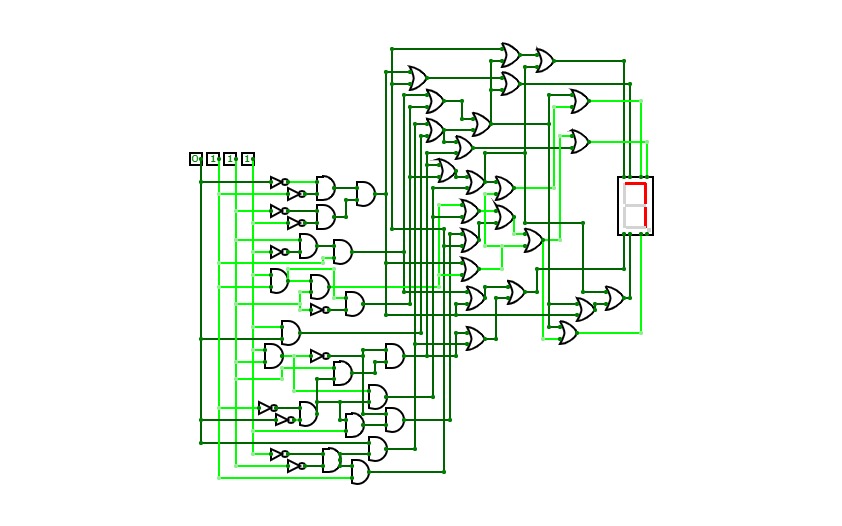
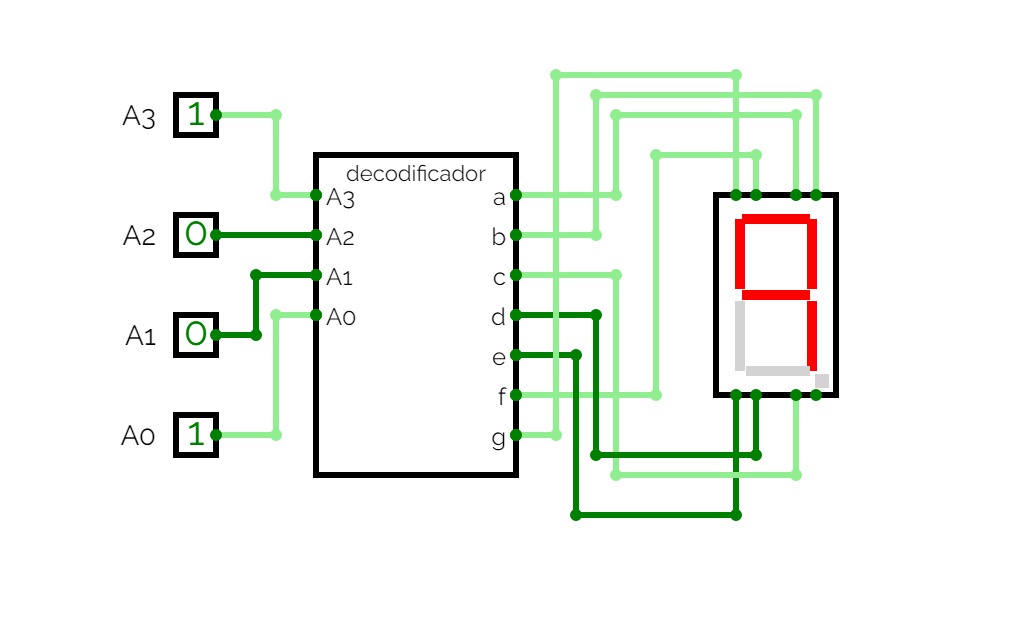
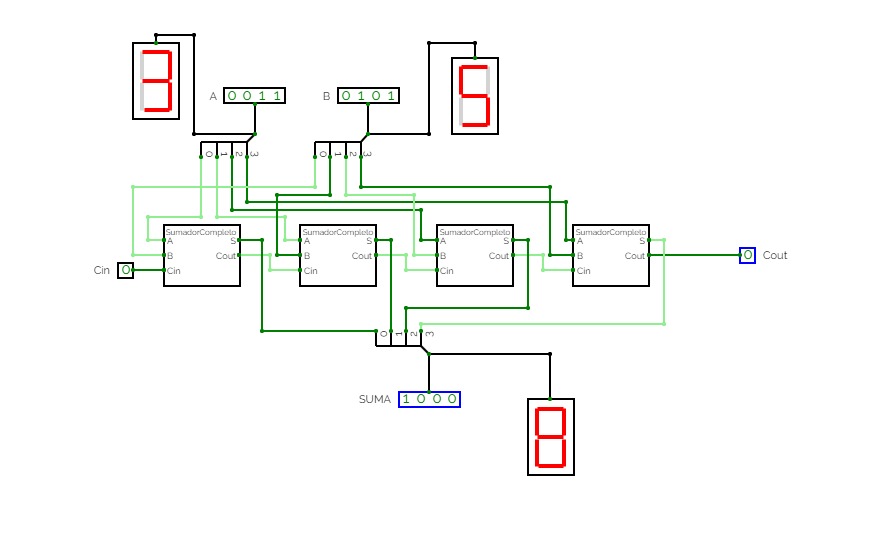
Binary to 7 Segment
Binary to 7 SegmentTranslates a binary form of a single digit number into its display in a seven segment format.
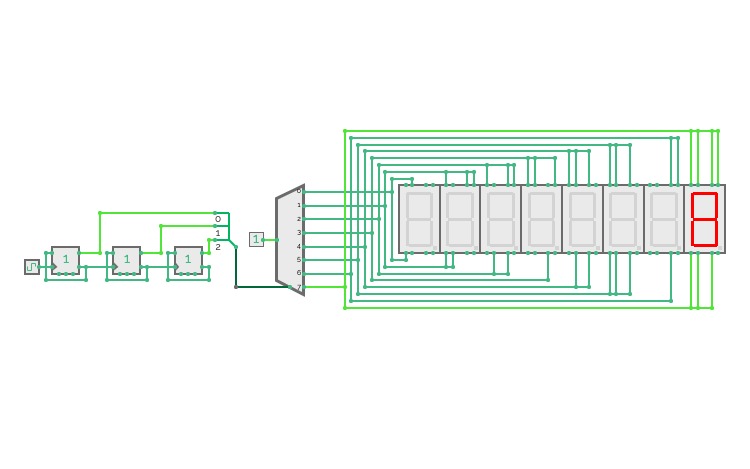
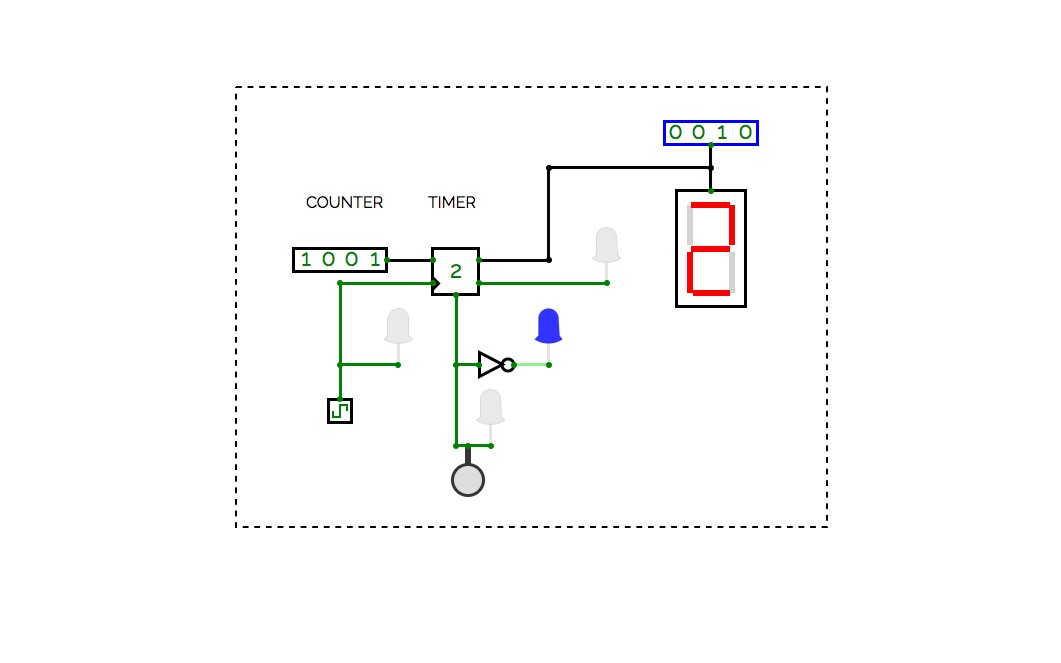
DEMUX Counter
DEMUX CounterEletrônica - Maria Laura Afonso
Eletrônica - Maria Laura AfonsoCustom 16 Bit CPU 34
Custom 16 Bit CPU 34To change sample program, copy a eeprom from the programs tab, and replace the one near the start of the circuit in main with it
to start it, toggle on and off the CLR button down by the clock circuit in Main
Explanation of how someone got many clock cycles per clock update:https://circuitverse.org/users/4699/projects/circuitverse-delay-introduction
Also after about 2 days I successfully coded and implemented Coonways game of life in here in a 16x16 grid(so each grid takes 256 entries in the storage and theres 2 of them)
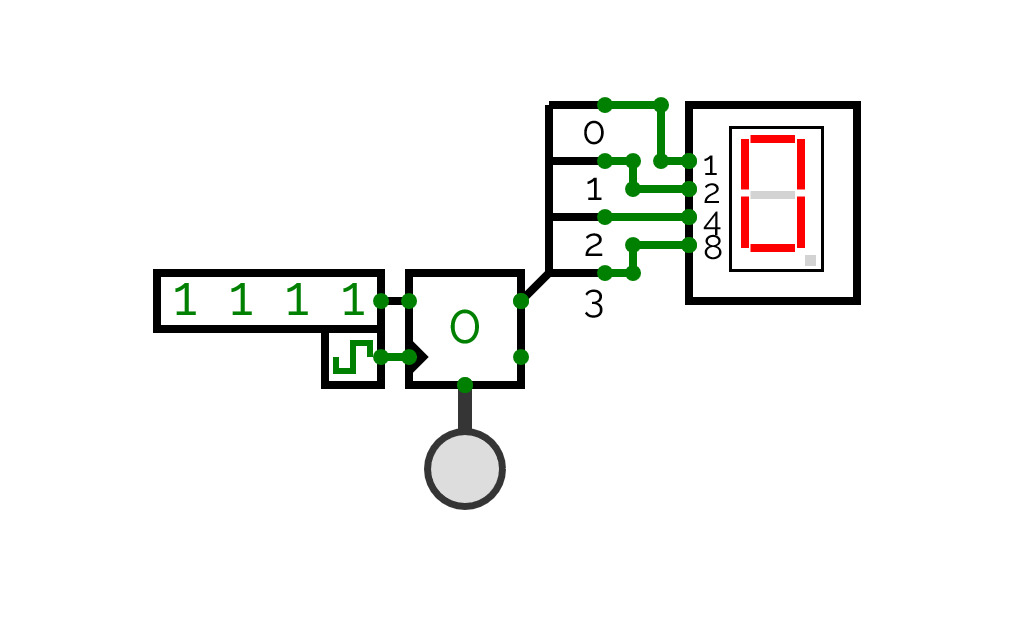
Moving Bar Display (2 bit)
Moving Bar Display (2 bit)This simple circuit displays decoded binary data in a Moving Bar format. One LED is illuminated when a binary 1 is applied, Two LEDs ar illuminated when a binary 2 is applied and Three LEDs are illuminated when binary 3 is applied.
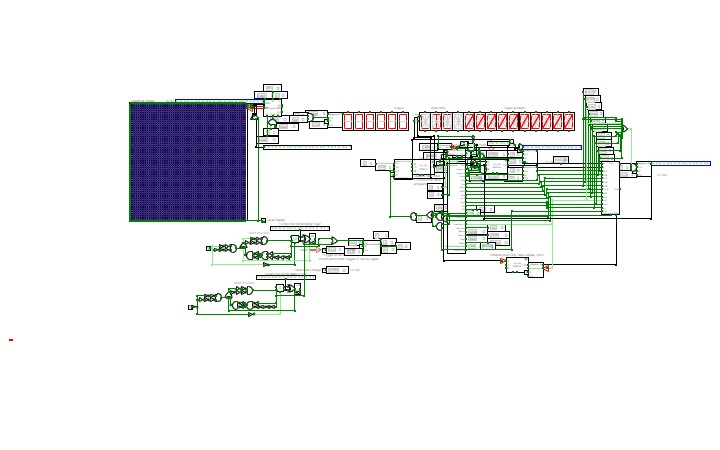
rixis combinox r1 cpu computer
rixis combinox r1 cpu computerAbout the Combinox R1:
This is the third 16-bit CPU I have made. Its new name was inspired by the new combinational code. It is also my first computer to feature a graphics and base ten display. As a result of its brand new architecture, code, and clock it is much faster than my previous CPUs.
Directions for use:
Choose the desired EEPROM program and insert it into the slot. First press the "RESET" button. Now press the "ON" button and enjoy your program.
Descriptions of programs:
blank: A blank EEPROM to be coded.
count up forever: Counts up by one until it reaches 65,535 then loops back to 0.
2+2: adds 2+2 and displays the output to the number display
transfer from keyboard to display: Displays the ascii value of whatever key is being entered on the keyboard.
random noise: Displays random noise on the screen.
Fibonacci: calculates the Fibonacci sequence
Credits:
Sanderokian Stfetoneri - clock
Sanderokian Stfetoneri - 16 bit division
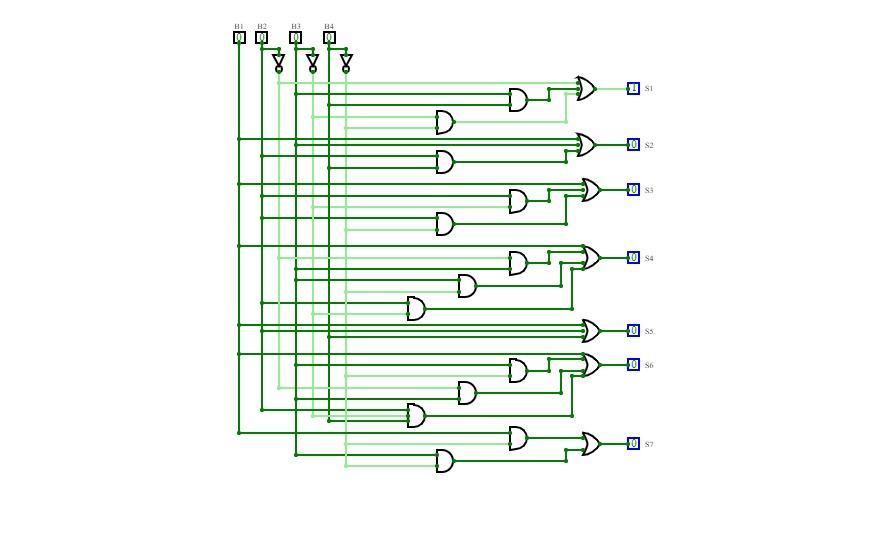
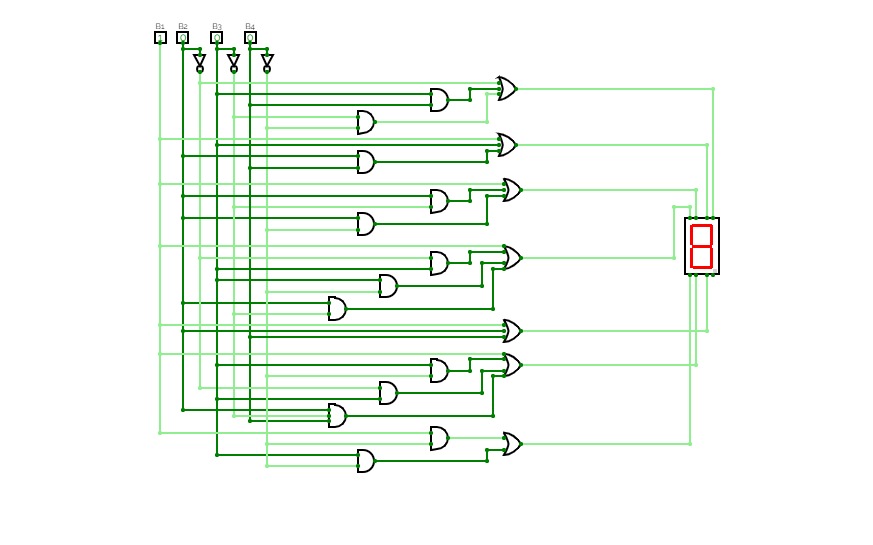
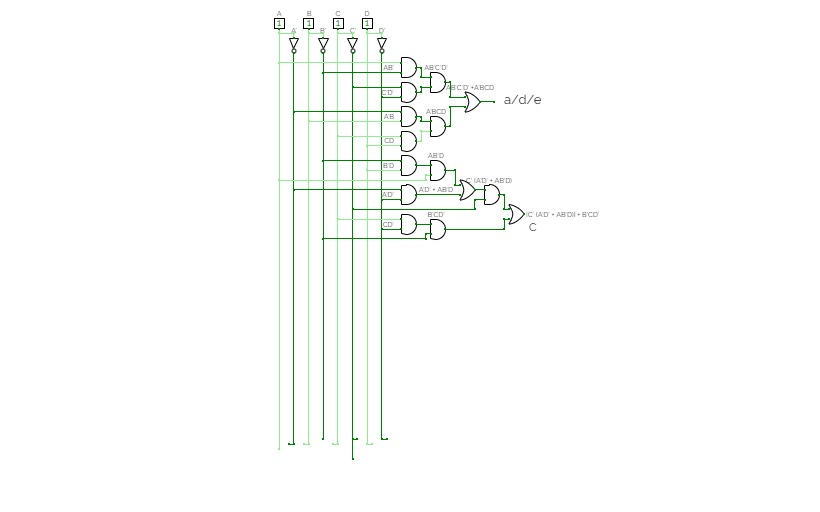
241202 BCD Converter
241202 BCD ConverterThe implementation of 4-bit BCD to display Converter subcircuit