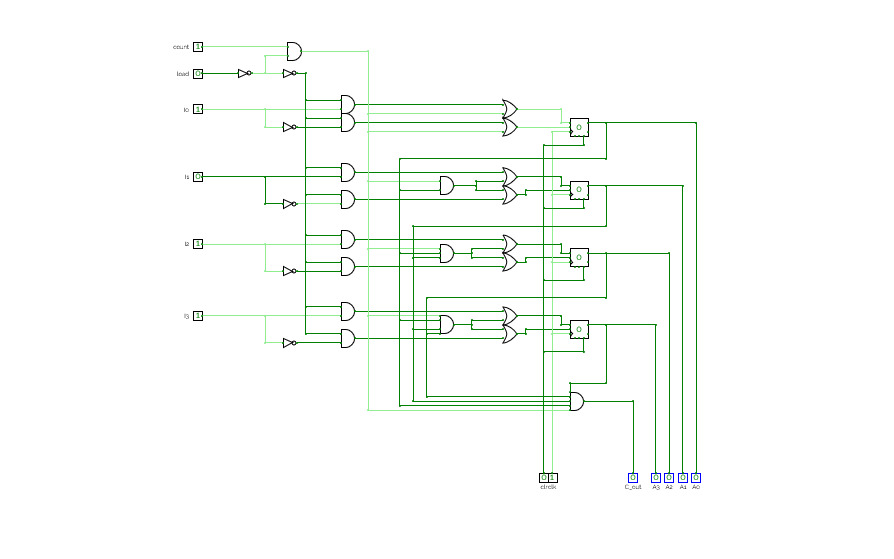
Four‐bit binary counter with parallel load
Four‐bit binary counter with parallel loadFour‐bit binary counter with parallel load. Do check it out. It has been tested!
A Full Subtractor is a combinational logic circuit that is designed to perform the subtraction of two binary numbers. It is considered "full" because it not only considers the subtraction of two binary inputs but also accounts for a borrow input from the previous stage. In other words, it can subtract three binary bits - minuend, subtrahend, and borrow - to produce the difference and a borrow output.
Multiplexer is a combinational circuit that has maximum of 2n data inputs, ‘n’ selection lines and single output line. One of these data inputs will be connected to the output based on the values of selection lines.
Since there are ‘n’ selection lines, there will be 2n possible combinations of zeros and ones. So, each combination will select only one data input. Multiplexer is also called as Mux.
4x1 Multiplexer
4x1 Multiplexer has four data inputs I3, I2, I1 & I0, two selection lines s1 & s0 and one output Y. The block diagram of 4x1 Multiplexer is shown in the following figure.

One of these 4 inputs will be connected to the output based on the combination of inputs present at these two selection lines. Truth table of 4x1 Multiplexer is shown below.
TRUTH TABLE
Selection LinesOutputS1S0Y00I001I110I211I3
From Truth table, we can directly write the Boolean function for output, Y as
Y=S1′S0′I0+S1′S0I1+S1S0′I2+S1S0I3Y=S1′S0′I0+S1′S0I1+S1S0′I2+S1S0I3
We can implement this Boolean function using Inverters, AND gates & OR gate. The circuit diagram of 4x1 multiplexer is shown in the following figure.
CIRCUIT DAIGRAM